A DHCP server is crucial for automating IP address assignment in networks. Troubleshooting DHCP server issues can seem daunting but is essential for network stability.
Understanding DHCP server troubleshooting can save time and prevent network disruptions. A DHCP server assigns IP addresses to devices, ensuring they communicate effectively. When this process fails, connectivity issues arise. By learning to identify and resolve common DHCP server problems, you can maintain a smooth and efficient network.
This guide will walk you through essential troubleshooting steps, helping you to diagnose and fix DHCP server issues. Keep reading to make your network reliable and hassle-free.
Introduction To Dhcp Server Issues
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server is vital for network operations. It assigns IP addresses to devices, ensuring smooth communication. But, issues can arise, causing disruptions. Understanding common DHCP problems and their quick fixes is crucial. Let’s dive into common DHCP server issues.
Common Problems
Several problems can affect DHCP server performance. One common issue is IP address conflicts. This happens when two devices receive the same IP address. Another problem is DHCP scope exhaustion. This occurs when all available IP addresses are assigned. Incorrect DHCP settings can also cause connectivity issues. It is important to identify these problems quickly.
Importance Of Quick Fixes
Quick fixes are essential for maintaining network stability. Downtime can lead to significant productivity losses. Resolving DHCP issues swiftly ensures devices stay connected. This keeps business operations running smoothly. It also prevents security vulnerabilities. Quick fixes help maintain a reliable network environment.
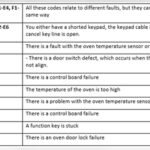
Identifying Dhcp Server Failures
Identifying DHCP server failures is crucial for maintaining a smooth network. These failures can disrupt connectivity, causing frustration for users. By following systematic steps, you can quickly identify and resolve DHCP server issues.
Initial Checks
Begin with the basics. Ensure the DHCP server is online and accessible. Verify the server’s IP address and network configuration. Confirm that the DHCP service is running. Use the command netstat -an | find "67" to check if the server listens on port 67.
Check the physical connections and network interfaces. Ensure that cables are connected properly. Test network connectivity using ping commands to the DHCP server and client machines. This helps in identifying any obvious network issues.
Error Logs Analysis
Error logs provide valuable insights. Access the Event Viewer on Windows servers. Look under Windows Logs and then System for DHCP-related errors. Common errors may include Event ID 1000 or Event ID 1010. These logs can point to specific problems with the DHCP service.
On Linux servers, use the command tail -f /var/log/syslog to monitor real-time logs. Look for DHCPD related entries. This helps in identifying issues like address pool exhaustion or network interface problems.
| Error ID | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | General DHCP service error |
| 1010 | DHCP address pool exhausted |
Network Connectivity Problems
Network connectivity problems can disrupt your workflow. They cause frustration and delays. To resolve these issues, it’s vital to troubleshoot effectively. This section will focus on common network connectivity problems with DHCP servers. We will look at connection testing and switch and router issues.
Connection Testing
Start by checking the physical connections. Ensure cables are securely connected. Verify that network devices have power. Use a network cable tester to check for faulty cables. Test the network connection on different devices. This helps to identify if the issue is device-specific.
Next, use the “ping” command. Open the command prompt and type “ping [IP address]”. This checks if the device can reach the DHCP server. If there is no response, the problem might be with the network path.
Switch And Router Issues
Inspect the switches and routers. Ensure they are powered on and working. Check the configuration settings. Incorrect settings can block network traffic.
Look for any hardware faults. Replace faulty devices if needed. Check for firmware updates. Outdated firmware can cause connectivity issues.
Examine the switch ports. Ensure the correct ports are in use. Verify that VLAN settings are correct. Misconfigured VLANs can block DHCP requests.
Ip Address Allocation Issues
IP address allocation issues can cause many problems on your network. DHCP servers assign IP addresses to devices on a network. But sometimes, things go wrong. This can disrupt your network and frustrate users. Let’s explore common issues and how to fix them.
Address Pool Exhaustion
Address pool exhaustion happens when the DHCP server runs out of IP addresses. This can occur if too many devices request addresses. The server has no more addresses to give out. Check the server’s address pool size. Increase the pool size if needed. Ensure you have enough IP addresses for all devices.
Monitor the number of devices on your network. If there are more devices than expected, adjust the pool size. Consider using a larger subnet to avoid exhaustion. Keep an eye on network usage trends. This helps you plan and prevent future issues.
Conflict Resolution
IP address conflicts occur when two devices have the same IP address. This can cause network issues and connectivity problems. To resolve conflicts, check the DHCP server’s lease table. Look for duplicate IP addresses. Release and renew leases for affected devices.
Ensure the DHCP server is the only device assigning IP addresses. Disable any rogue DHCP servers on the network. Use IP address conflict detection tools. These tools help identify and resolve conflicts quickly. Keeping your network organized helps prevent conflicts.
Dhcp Scope Configuration Errors
Dealing with DHCP scope configuration errors can be a common issue for network administrators. These errors can lead to significant network disruptions. Understanding and resolving these errors is crucial for maintaining network efficiency and connectivity. This section will cover important aspects of DHCP scope configuration errors.
Scope Settings Review
Reviewing the scope settings is the first step in troubleshooting DHCP scope configuration errors. Ensure that the DHCP scope is correctly defined and active. Check the range of IP addresses available for assignment. Verify that the start and end IP addresses are within the same network.
Use the following checklist to review the settings:
- Ensure the scope is active.
- Verify the start and end IP addresses.
- Check if the address range is correct.
- Ensure there are no overlaps with other scopes.
Subnet Mask Issues
Subnet mask issues are common in DHCP scope configuration. Incorrect subnet masks can cause IP address conflicts. Ensure that the subnet mask matches the network configuration.
Here is how to check for subnet mask issues:
- Ensure the subnet mask is consistent across devices.
- Verify that the subnet mask aligns with the network design.
- Check for any typos or incorrect entries.
- Ensure that the subnet mask allows sufficient hosts.
To avoid subnet mask issues, use the following table as a guide:
| Subnet Mask | Number of Hosts |
|---|---|
| 255.255.255.0 | 254 |
| 255.255.254.0 | 510 |
| 255.255.252.0 | 1022 |
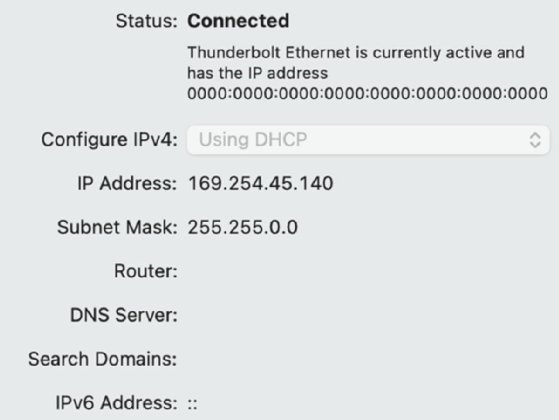
Client-side Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting DHCP server issues from the client side can be challenging. Yet, it is a crucial step in maintaining network connectivity. Below are some key actions to take when troubleshooting from the client side.
Client Configuration
First, ensure the client’s network settings are correct. Verify that the client is set to obtain an IP address automatically. This setting allows the DHCP server to assign an IP address to the client. Check the network adapter settings in the control panel or system preferences. Make sure the adapter is enabled and functioning properly.
Release And Renew Ip Address
Releasing and renewing the IP address can often resolve connectivity issues. Open the command prompt or terminal on the client device. Type ipconfig /release and press enter. This command releases the current IP address. Next, type ipconfig /renew and press enter. This command requests a new IP address from the DHCP server. Check if the client can now connect to the network.
Dhcp Relay Agent Problems
The DHCP relay agent is essential for forwarding requests between clients and servers. Problems with the relay agent can disrupt network connectivity. Understanding and fixing these issues is crucial.
Relay Agent Configuration
Incorrect configuration is a common cause of relay agent issues. Ensure the relay agent’s IP address is correctly set. Check the relay agent settings in your router or switch. Verify that the relay agent is enabled and pointing to the correct DHCP server. Misconfigurations can stop DHCP requests from reaching the server.
Communication Failures
Network communication problems can affect the relay agent. Inspect network cables and connections. Confirm that routers and switches are functioning correctly. Examine firewall settings to ensure they are not blocking DHCP traffic. Check for network congestion or hardware failures. Communication issues can prevent the relay agent from forwarding requests.
Credit: www.techtarget.com
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
When dealing with DHCP server issues, basic methods sometimes fall short. Advanced techniques can pinpoint hidden problems. These methods often involve deeper analysis and specialized tools.
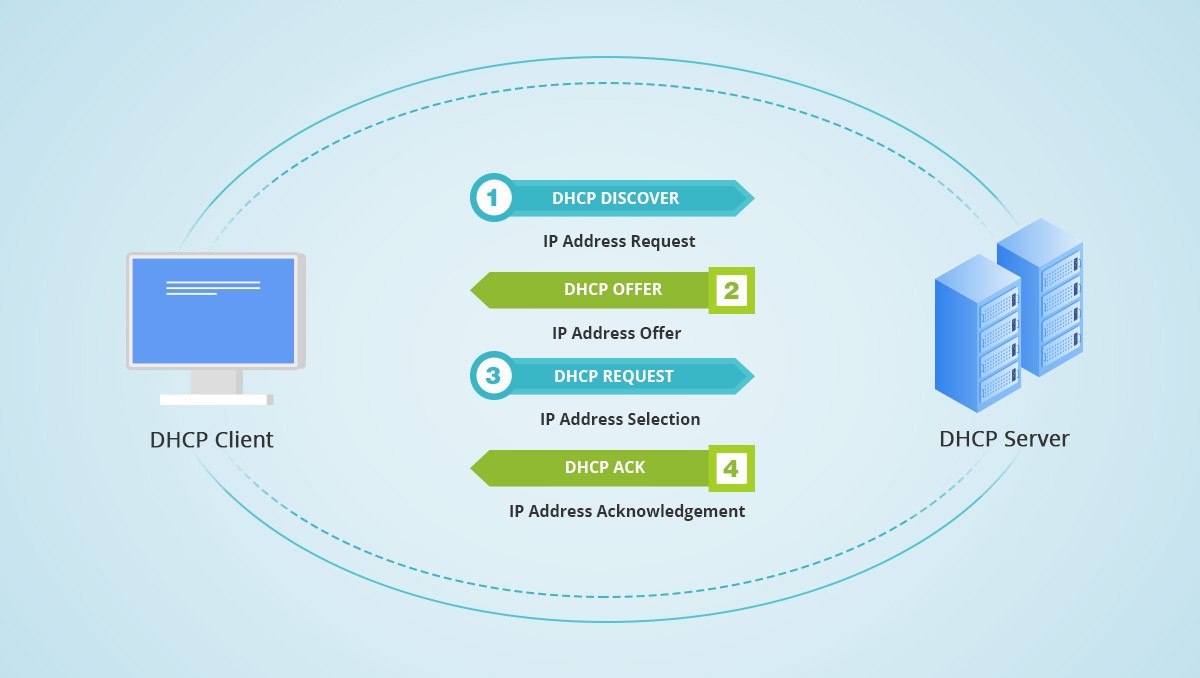
Packet Sniffing
Packet sniffing helps track data packets between devices and the DHCP server. This technique reveals whether packets are reaching their destination. Use tools like Wireshark to capture and analyze network traffic. Look for DHCP Discover, Offer, Request, and Acknowledge messages. Missing or malformed packets indicate issues.
Server Performance Monitoring
Server performance monitoring checks the health of your DHCP server. Use tools like Nagios or SolarWinds to monitor server load, memory, and CPU usage. High load or resource usage can slow down DHCP services. Regular monitoring helps detect problems early. Ensure your server is not overwhelmed.
Preventive Measures
Preventive measures are crucial for maintaining a healthy DHCP server. These steps help avoid issues before they disrupt network operations. Regular maintenance and backup procedures ensure the system runs smoothly.
Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance involves checking server logs. This helps identify potential issues early. Update the DHCP server software frequently. This ensures you have the latest security patches and features. Clean up old leases and reservations. This keeps the DHCP database manageable and efficient.
Backup And Restore Procedures
Backup procedures are vital for disaster recovery. Always keep a recent backup of your DHCP server settings. Store these backups in a secure location. Practice restoring from backups regularly. This ensures you can recover quickly during a failure. Regular backups protect against data loss and minimize downtime.
Credit: www.linkedin.com

Credit: www.trio.so
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is A Dhcp Server?
A DHCP server automatically assigns IP addresses to devices on a network. It makes network management easier.
How Do I Check If Dhcp Is Working?
Use the “ipconfig” command on Windows or “ifconfig” on Linux. Look for the IP address information.
Why Is My Dhcp Server Not Assigning Ip Addresses?
Check for network issues, server configuration errors, or exhausted IP address pools. Restart the DHCP service.
How Can I Fix Dhcp Server Issues?
Restart the server, check network connections, and verify configurations. Ensure the DHCP service is running properly.
What Are Common Dhcp Server Errors?
Common errors include IP conflicts, DHCP service failure, and misconfigured settings. Check logs for specific error messages.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting a DHCP server can seem complex, but it’s manageable. Follow the steps outlined in this guide. Check connections, configurations, and software updates regularly. Document all changes and solutions for future reference. Stay patient and systematic. With practice, resolving DHCP issues becomes easier.
Happy troubleshooting!