Understanding manifold gauge readings is vital for troubleshooting R134A AC systems. Accurate readings help identify issues and ensure efficient cooling.
Manifold gauge sets are essential tools for anyone working with air conditioning systems. They measure the pressures within the system, offering insights into its performance and health. R134A is the most common refrigerant used in modern vehicles, making it crucial to understand how to interpret these readings.
Knowing the correct pressures can help diagnose problems like leaks, blockages, or failing components. This guide will walk you through the basics of manifold gauge readings for R134A AC systems, helping you troubleshoot and maintain your AC system effectively. Whether you’re a professional or a DIY enthusiast, mastering this skill is essential for keeping your vehicle’s AC in top shape.
Introduction To Manifold Gauge Readings

Manifold gauge readings are crucial for maintaining your car’s air conditioning system. They help in diagnosing issues and ensuring the system runs efficiently. Understanding these readings can save you time and money.
With R134A AC systems, knowing how to read manifold gauges is essential. It allows you to troubleshoot problems quickly. This guide will help you understand the basics.
Purpose Of Manifold Gauges
Manifold gauges measure the pressure in your AC system. They help identify issues like leaks or blockages. High and low-pressure readings indicate different problems.
These gauges provide a snapshot of your AC’s health. They help in determining the right amount of refrigerant. Proper readings ensure the system works efficiently.
Components Of A Manifold Gauge
A manifold gauge set consists of three main components: gauges, hoses, and valves. The gauges show the pressure readings. There are two gauges, one for high pressure and one for low pressure.
The hoses connect the gauges to the AC system. Each hose is color-coded for easy identification. Blue for low pressure, red for high pressure, and yellow for refrigerant.
The valves control the flow of refrigerant. They allow you to add or remove refrigerant from the system. Proper use of these components is key to accurate readings.
Basics Of R134a Refrigerant
The basics of R134A refrigerant are essential for understanding AC pressure troubleshooting. This refrigerant is widely used in automotive air conditioning systems. Knowing its properties and applications helps diagnose issues effectively.
R134a Properties
R134A is a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) refrigerant. It has a boiling point of -15.34 degrees Fahrenheit. It does not contain chlorine, making it ozone-friendly. It is non-flammable and has low toxicity. These properties make it a safe choice for AC systems.
Why R134a Is Commonly Used
R134A replaced R12 due to environmental concerns. R12 harmed the ozone layer. R134A is more eco-friendly. It is also efficient in cooling. It provides consistent performance under various conditions. Mechanics and manufacturers prefer it for its reliability and safety.
Understanding AC Pressure Readings
Understanding AC pressure readings is essential for diagnosing R134A AC systems. These readings help identify issues within the system. They can indicate if the system is functioning correctly or if there are problems like leaks or blockages.
AC systems have two main pressure sides: the high side and the low side. Each side has its own pressure range. Knowing these ranges is key to troubleshooting and maintaining your AC system.
High-side Pressure Readings
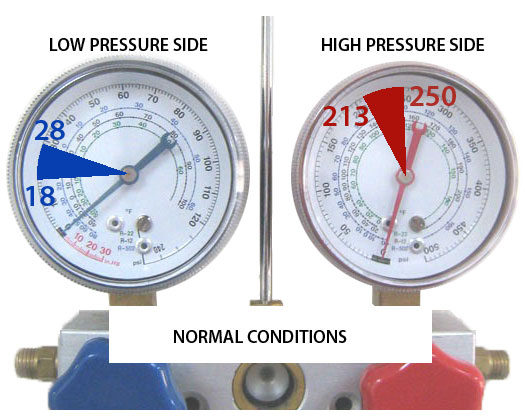
The high side of the AC system carries the refrigerant in a high-pressure state. Normal high-side pressure readings range from 150 to 250 psi. Readings above this range can indicate blockages or overcharging. Readings below this range may suggest refrigerant leaks or a failing compressor.
To check high-side pressure, connect the red hose of the manifold gauge to the high-side port. Ensure the system is running at the correct settings. Record the reading after the system stabilizes. Compare the reading with the standard range to diagnose potential issues.
Low-side Pressure Readings
The low side of the AC system carries the refrigerant in a low-pressure state. Normal low-side pressure readings range from 25 to 45 psi. Readings above this range can indicate overcharging or a failing expansion valve. Readings below this range may suggest refrigerant leaks or a faulty compressor.
To check low-side pressure, connect the blue hose of the manifold gauge to the low-side port. Ensure the system is running at the correct settings. Record the reading after the system stabilizes. Compare the reading with the standard range to diagnose potential issues.
Regularly monitoring these readings can help maintain your AC system. It can prevent major issues and ensure efficient operation. Always refer to your vehicle’s manual for specific pressure ranges.
Normal Operating Pressures For R134a
Understanding the normal operating pressures for R134A is vital. It helps in diagnosing AC system issues. R134A refrigerant is used in many modern vehicles. Knowing the ideal pressures ensures the system works efficiently.
Ideal High-side Pressures
The high-side pressure is on the discharge side of the compressor. For R134A, this pressure should be between 150 to 250 psi. This range ensures the refrigerant moves effectively. It keeps the vehicle’s interior cool.
Exceeding this range can indicate a problem. It might be a blocked condenser. Or an overcharged system. Both can affect cooling performance. Regular checks can prevent these issues.
Ideal Low-side Pressures
The low-side pressure is on the suction side of the compressor. For R134A, it should be between 25 to 45 psi. This ensures the refrigerant absorbs heat inside the car. Then releases it outside efficiently.
Too low or too high pressures can signal issues. Low pressure might mean a refrigerant leak. High pressure could indicate a faulty expansion valve. Keeping an eye on these readings is crucial.
Manifold Gauge Readings R134A AC Pressure Troubleshooting For Common AC Pressure Issues
Understanding common AC pressure issues is important for anyone working with R134A refrigerant. Knowing the symptoms of high and low pressure can help troubleshoot and maintain your AC system. This guide will cover the basics of high and low pressure symptoms.
High Pressure Symptoms
High pressure in the AC system usually indicates a blockage or overcharging. Symptoms include:
- Warm air blowing from the vents
- Compressor cycling on and off quickly
- Hissing or bubbling noises
High pressure can damage the compressor. It may also cause leaks in the system. Regular maintenance can prevent these issues.
Low Pressure Symptoms
Low pressure often means a refrigerant leak or a faulty compressor. Symptoms include:
- Weak airflow from the vents
- Cold air that warms up quickly
- Frost on the AC lines
Low pressure can lead to poor cooling performance. It can also make the compressor work harder, leading to wear and tear.
To keep your AC system running smoothly, use a manifold gauge to check the pressure regularly. This tool helps identify issues early, saving time and money.
Manifold Gauge Readings R134A AC High Pressure Problems

Diagnosing high pressure problems in your R134A AC system can be crucial. High pressure can indicate issues that need immediate attention. Understanding the reasons behind high pressure can help you fix them quickly.
Causes Of High Pressure
Several factors can cause high pressure in your AC system. One common cause is an overcharged system. Too much refrigerant can increase pressure. Another cause could be a malfunctioning condenser fan. If the fan is not working, it cannot cool the refrigerant. Blockages in the system can also lead to high pressure. Dirt and debris can restrict the flow. Lastly, high ambient temperatures can add to the problem. The hotter the environment, the harder the system works.
Solutions For High Pressure
First, check the refrigerant levels. Ensure the system is not overcharged. If it is, remove the excess refrigerant. Next, inspect the condenser fan. Make sure it is operating correctly. Clean the fan if needed. Also, look for blockages in the system. Clean or replace any clogged parts. Lastly, try to cool down the environment. Parking in the shade can help reduce ambient temperatures.
Manifold Gauge Readings R134A AC Low Pressure Problems
Diagnosing low pressure problems in an R134A AC system can be challenging. Understanding the causes and solutions helps maintain optimal performance. Low pressure often means the system isn’t cooling properly. This guide will help you troubleshoot and fix these issues.
Causes Of Low Pressure
There are several reasons for low pressure in an R134A AC system. Identifying the correct cause is crucial for effective troubleshooting.
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Refrigerant Leak | A leak in the system can reduce refrigerant levels, causing low pressure. |
| Clogged Expansion Valve | A clogged valve can restrict refrigerant flow, leading to low pressure. |
| Faulty Compressor | A malfunctioning compressor can’t maintain proper pressure levels. |
| Improper Refrigerant Charge | Incorrect refrigerant amounts can cause pressure issues. |
Solutions For Low Pressure
Once you identify the cause, you can apply the right solution. Here are common fixes for low pressure problems.
- Check for Leaks: Use a leak detection tool to find and repair any leaks.
- Clean or Replace the Expansion Valve: Inspect the valve for clogs and clean or replace it if needed.
- Test and Replace the Compressor: If the compressor is faulty, replace it to restore proper pressure.
- Recharge the System: Make sure the refrigerant charge is correct. Add or remove refrigerant as needed.
Diagnosing and fixing low pressure issues ensures your AC system works efficiently. Always follow safety guidelines when working with refrigerants and AC systems.
Safety Precautions
Working with R134A manifold gauges requires strict safety precautions. Mishandling refrigerant or gauges can lead to serious injury. Below, we will discuss essential safety measures to follow.
Handling Refrigerant Safely
Refrigerant R134A is a chemical that can be harmful. Always wear protective gear when handling it. This includes gloves and safety goggles. Exposure to skin can cause frostbite. Inhalation can be dangerous. Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fumes.
Never release refrigerant into the atmosphere. Use proper equipment to collect and recycle it. This helps protect the environment and follows legal guidelines.
Using Manifold Gauges Properly
Manifold gauges are tools that measure AC pressure. Incorrect use can cause injury or damage to the AC system. Before starting, read the user manual thoroughly.
Check the condition of your gauges. Ensure there are no leaks or damage. Connect the gauges securely to the AC system. Make sure all connections are tight to avoid leaks.
Follow these steps to use manifold gauges:
- Turn off the AC system before connecting gauges.
- Attach the low-pressure hose to the low-pressure port.
- Attach the high-pressure hose to the high-pressure port.
- Open the valves slowly to avoid pressure spikes.
- Monitor readings carefully and adjust as needed.
Always disconnect gauges in reverse order. This prevents sudden pressure release.
Maintenance Tips For Manifold Gauge Readings R134A AC Pressure
Keeping your R134A AC system in top shape is crucial. Proper maintenance can prevent costly repairs. It also ensures the system runs efficiently. Below are some essential tips.
Regular Maintenance Practices
Regular maintenance is the key to a long-lasting AC system. Follow these simple steps:
- Check Refrigerant Levels: Ensure the R134A levels are optimal. Low levels can reduce cooling efficiency.
- Inspect for Leaks: Use a leak detector. Leaks can lead to refrigerant loss and system damage.
- Clean the Condenser: Dirt and debris can clog the condenser. Use a soft brush or compressed air to clean it.
- Check Hoses and Connections: Look for signs of wear or damage. Replace any faulty parts immediately.
- Test System Pressure: Use a manifold gauge to check both high and low pressures. This helps in early detection of issues.
When To Seek Professional Help
Some issues require expert attention. Here are signs that you need professional help:
- Unusual Noises: Strange sounds can indicate mechanical problems. A professional can diagnose and fix it.
- Poor Cooling Performance: If your AC isn’t cooling well, it might need a thorough check-up.
- High Pressure Readings: Consistently high readings can signal a major issue. This needs immediate attention.
- Refrigerant Leaks: Only a certified technician should handle refrigerant leaks. Improper handling can be dangerous.
- Electrical Issues: If the AC system isn’t turning on, it could be an electrical problem. This requires a professional diagnosis.
Regular maintenance and knowing when to seek help can keep your AC system running smoothly. Stay proactive and ensure your comfort all year round.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Do Manifold Gauge Readings Mean?
Manifold gauge readings show the pressure levels in your AC system. They help diagnose issues.
How To Read R134a Manifold Gauge?
Attach the gauges to the service ports. Red for high pressure, blue for low pressure.
What Are Normal R134a Pressure Readings?
Normal readings: 25-45 psi on low side, 200-250 psi on high side.
What Causes High Ac Pressure Readings?
High readings may be due to overcharging, a clogged condenser, or a faulty compressor.
Why Is My Ac Not Cooling Properly?
Low pressure readings could indicate a refrigerant leak or a problem with the expansion valve.
Conclusion
Understanding manifold gauge readings for R134A is essential for AC troubleshooting. Regular maintenance ensures your system runs efficiently. Always check for leaks and proper pressure levels. Use the right tools to get accurate readings. By following these steps, you can keep your AC in good shape.
Remember, a well-maintained AC provides better cooling and lasts longer. Keep learning and stay informed about your AC system. This knowledge helps you avoid costly repairs and ensures comfort year-round. Happy troubleshooting!