Are you ready to sharpen your networking skills and tackle real-world problems head-on? The Packet Tracer Troubleshooting Challenge is designed to push your ability to document and understand complex networks like a pro.
By carefully documenting the network, you’ll unlock the secrets behind connectivity issues and device configurations that often trip up many IT professionals. This isn’t just about fixing problems—it’s about building a clear, step-by-step roadmap that guides you through every twist and turn in the network.
Stick with me, and you’ll discover practical tips and proven strategies that will make troubleshooting faster, easier, and more effective for your next challenge. Your network mastery starts here!

Credit: www.scribd.com
Network Documentation Basics
Network documentation is essential for managing and troubleshooting networks effectively. It provides a clear map of the network’s design and setup. Proper documentation helps identify problems quickly and reduces downtime. It also supports smooth communication among IT teams and stakeholders. Understanding the basics of network documentation ensures better control over network challenges and changes.
Purpose Of Documentation
Documentation records the structure and details of a network. It helps IT staff track devices, connections, and configurations. Well-documented networks speed up problem-solving and maintenance. It also supports training new team members. Without documentation, network issues take longer to fix and cause more disruptions.
Key Elements To Record
Start with device names and IP addresses. Note the type of equipment used, such as routers and switches. Record connection paths and port numbers. Include configuration settings and software versions. Keep track of network topologies and security policies. These elements provide a full picture of the network environment.
Tools For Documentation
Use diagramming tools like Microsoft Visio or draw.io for network maps. Text editors or spreadsheets help list device details and settings. Automated tools can scan and report network status. Cloud-based platforms allow easy updates and sharing. Choose tools that fit your team’s size and skill level for best results.
Preparing For Troubleshooting
Preparing for troubleshooting is a crucial step in solving network problems using Packet Tracer. It sets the foundation for a clear and efficient approach. Without proper preparation, identifying the root cause becomes difficult and time-consuming.
This stage involves collecting key details about the network. You need to understand the devices involved and how they connect. Proper documentation here will guide you throughout the troubleshooting process.
Gathering Network Information
Start by collecting all available information about the network. Note IP addresses, subnet masks, and default gateways. Record device names and operating system versions. This data helps pinpoint where issues may arise and what tools to use.
Identifying Network Devices
List all network devices such as routers, switches, and hosts. Check for device roles and configurations. Understanding each device’s function aids in isolating problems. Confirm device status and any error indicators visible in Packet Tracer.
Mapping Network Topology
Create a visual map of the network layout. Show how devices connect and communicate. Use diagrams to highlight links and paths. A clear topology map helps track data flow and locate failures quickly. It serves as a reference during troubleshooting steps.
Testing Network Connectivity
Testing network connectivity is a vital step in troubleshooting networks using Packet Tracer. It helps confirm if devices can communicate with each other across the network. Checking connectivity quickly reveals where problems exist.
This process involves several simple commands and checks to verify if the network setup works as expected. Each test provides clues about device reachability and configuration issues. Understanding these tests improves your ability to fix network problems effectively.
Using Ping And Traceroute
Ping sends small packets to a target device and waits for a reply. It tests if the device is reachable and measures response time. If ping fails, the device may be offline or blocked by a firewall.
Traceroute maps the path packets take from your device to the target. It shows all intermediate routers. This helps find where communication breaks down in the network route.
Verifying Ip Configurations
Check each device’s IP address, subnet mask, and other settings. Correct IP settings ensure devices are on the right network segment. Wrong IPs cause communication failures or routing issues. Use commands like ipconfig or ifconfig to view these details.
Checking Default Gateways
The default gateway directs traffic from a device to other networks. Verify each device has the correct gateway IP set. A wrong or missing gateway blocks traffic beyond the local network. Testing gateway reachability confirms if routing is possible.
Analyzing Device Configurations
Applying troubleshooting methodology is essential for solving network issues effectively in Packet Tracer. It involves a clear, step-by-step approach that guides you through the problem-solving process. This method helps you avoid guesswork and reduces downtime. By following structured steps, you can find and fix problems faster.
The process begins with understanding the symptoms. Then, you develop possible causes and test them one by one. Once you confirm the cause, you apply the correct fix. This approach improves accuracy and ensures lasting solutions for network problems.
Identifying Problems
Start by observing the network carefully. Look for error messages, connection failures, or unusual behavior. Check device lights and status indicators. Ask users about the issue and when it started. Gather as much information as possible. Clear identification helps narrow down the possible causes quickly.
Forming Theories
Based on the gathered data, think about what might cause the problem. Consider common issues like cable problems, configuration errors, or IP conflicts. List the most likely reasons. Prioritize these theories by likelihood and ease of testing. This step helps focus your efforts on the most probable causes.
Testing Solutions
Start testing your theories one at a time. Use tools like ping, traceroute, or Packet Tracer simulations. Check if changes fix the issue or if the problem persists. Testing prevents unnecessary changes and keeps troubleshooting organized. It also confirms the actual cause without assumptions.
Implementing Fixes
Once you find the root cause, apply the needed fix carefully. Update configurations, replace faulty hardware, or reset devices as required. After fixing, verify the network works properly again. Document the fix for future reference. Proper implementation ensures the problem does not return quickly.
Common Network Issues
Documenting troubleshooting steps is essential for effective network problem-solving. It helps track what actions you take and what results occur. Clear documentation allows you to revisit past steps and avoid repeating mistakes. It also supports sharing knowledge with others working on the network.
Accurate records simplify the troubleshooting process. They make it easier to identify patterns and recurring issues. Keeping detailed notes saves time and improves the success rate of fixing problems.
Recording Observations
Start by writing down all symptoms and error messages you notice. Note the exact time and conditions when the issue appears. Observe device behaviors carefully and describe them clearly. Record any changes or unusual events related to the problem. This information forms the foundation of your troubleshooting.
Updating Network Diagrams
Keep your network diagrams current by adding new devices and connections. Mark any changes made during troubleshooting on the diagrams. Highlight affected areas and paths involved in the issue. Updated diagrams provide a visual reference to understand the network layout. They help pinpoint where problems may originate.
Maintaining Logs
Create logs that list each troubleshooting step taken. Include the tools and commands used along with their outputs. Write down which solutions you tried and their effects. Maintain these logs in an organized and accessible format. Logs serve as a history to review and learn from past troubleshooting efforts.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Applying Troubleshooting Methodology
Documentation plays a key role in solving network challenges in Packet Tracer. It acts as a clear map, showing device setups and connection paths. Well-kept records save time and reduce errors during troubleshooting. Using documentation helps to focus on the right areas quickly. It also supports better understanding of the network’s behavior and issues.
Guiding Troubleshooting Efforts
Documentation points out where to start looking for problems. It lists all devices, their IP addresses, and link types. Troubleshooters can use this data to check if devices are correctly configured. It also helps to confirm if cables and ports match the design. This focus avoids random checking and speeds up finding faults.
Identifying Patterns
Keeping logs and notes uncovers repeating problems in the network. For example, if the same device fails often, it may need replacement. Patterns in errors or slow connections show weak points in the design. Recognizing these trends helps in planning fixes that stop issues from coming back. Documentation makes these patterns easy to spot.
Avoiding Recurring Issues
Good documentation records past fixes and their results. This information prevents repeating the same mistakes. It also guides on what solutions worked best before. By reviewing history, teams can apply proven methods fast. This reduces downtime and keeps the network stable over time.
Documenting Troubleshooting Steps
Advanced troubleshooting in Packet Tracer requires a keen eye and solid techniques. These tips help solve tough network problems faster. Focus on key areas to keep the network stable and efficient. The following sections cover critical topics for complex network issues.
Remote Device Access
Accessing devices remotely saves time and effort. Use secure methods like SSH instead of Telnet for better safety. Check device IP addresses and login credentials before connecting. Make sure remote access settings are enabled on routers or switches. Test connectivity with simple ping commands first. This approach prevents wasted time on unreachable devices.
Dynamic Trunking Issues
Trunk ports carry multiple VLANs between switches. Mismatched trunk settings cause traffic loss or loops. Verify trunk mode settings on both ends—use “dynamic desirable” or “dynamic auto” carefully. Confirm allowed VLANs match on each side. Use “show interfaces trunk” to check trunk status and VLAN tags. Fix any mismatches quickly to restore proper communication.
Interpreting Complex Logs
Logs contain clues to network problems but can be overwhelming. Focus on error messages and timestamps for relevant events. Filter logs by severity or device to narrow down issues. Learn common log terms like “link down,” “authentication failure,” or “interface reset.” Use logs alongside other tools for a full picture. Clear logs regularly to avoid clutter and confusion.
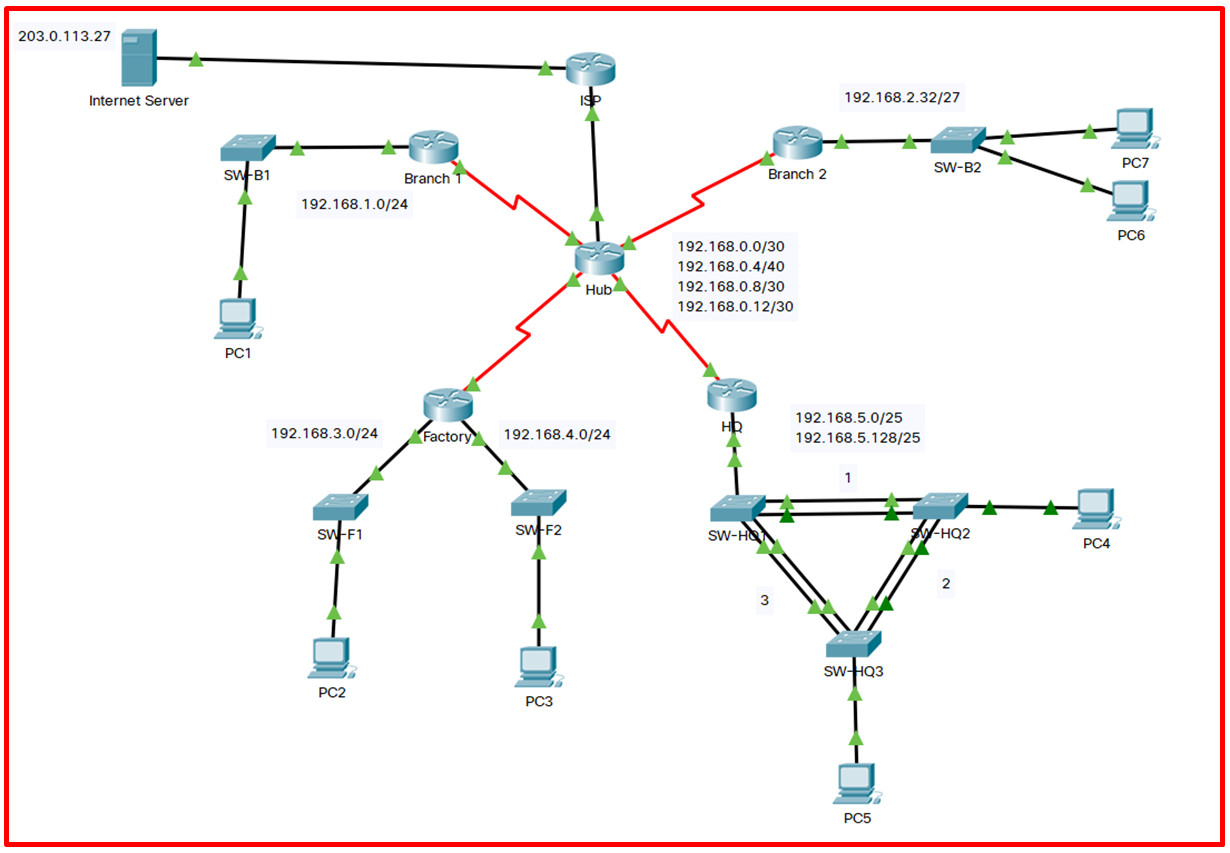
Credit: itexamanswers.net
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The 7 Steps Of Network Troubleshooting?
The 7 steps of network troubleshooting are: identify the problem, establish a theory, test the theory, plan a solution, implement the fix, verify functionality, and document the process.
When Troubleshooting Network Issues Using The Comptia Network+ Troubleshooting Method?
The CompTIA Network+ troubleshooting method involves identifying the problem, forming and testing a theory, planning and implementing a solution, or escalating if needed.
When You Are Troubleshooting A Network Problem, What Is One Of The First Steps You Should Take In The Process?
One of the first steps in troubleshooting a network problem is to check physical connections and verify device power status.
How To Troubleshoot A Network Connectivity Problem?
Check physical connections and device status first. Restart modem, router, and device. Verify IP settings and run network diagnostics. Test connectivity on another device. Adjust Wi-Fi channels if needed. Document findings and escalate if unresolved.
What Is Packet Tracer Troubleshooting Challenge?
Packet Tracer troubleshooting challenge is a practice activity. It helps users identify and fix network issues in a simulated environment. This builds real-world networking skills.
Conclusion
Documenting the network carefully helps solve problems faster. Write clear notes about devices and connections. Check each step to find the cause of issues. Use diagrams to see how parts link together. Good records make troubleshooting easier and less stressful.
Practice with Packet Tracer to improve your skills daily. Keep learning and stay patient during challenges. This habit builds confidence and helps fix networks quickly.