Is your solenoid valve acting up—refusing to open, leaking, or making strange noises? If so, you’re not alone.
Solenoid valve issues can bring your entire system to a halt, causing frustration and costly downtime. But before you call in a technician, there are simple checks and fixes you can try yourself. In this guide, you’ll discover how to spot common solenoid valve problems, understand what causes them, and learn straightforward troubleshooting steps to get your valve working smoothly again.
Keep reading, and you’ll gain the confidence to tackle these issues head-on, saving time and money while keeping your equipment running at peak performance.
Common Failure Symptoms
Solenoid valves may fail due to many reasons. Recognizing common failure symptoms helps fix problems quickly. These symptoms affect valve function and overall system health. Early detection reduces downtime and repair costs. Below are typical signs to watch for during troubleshooting.
Valve Operation Issues
The valve may fail to open or close fully. Sometimes it moves slowly or sticks intermittently. This can cause flow problems in the system. Dirt, debris, or corrosion often block valve parts. Incorrect voltage or pressure also affects movement. Timely inspection prevents further damage.
Leaks
Leaks appear as fluid escaping from valve seals or body. Internal leaks cause unintended flow inside the system. Worn or damaged seals usually cause these leaks. Poor installation or cracked valve parts also lead to leaks. Leaks reduce system efficiency and may cause hazards.
Noise And Vibration
Unusual sounds like humming, buzzing, or thumping indicate trouble. Rapid vibration may come from internal wear or debris. Pressure irregularities also cause noise and shaking. These symptoms suggest the valve needs cleaning or repair. Ignoring noise can worsen damage over time.
Electrical Problems
Burnt coils stop the valve from working properly. Loose or broken wires cause intermittent operation. Incorrect voltage supply damages electrical components. Testing coils and wiring helps locate faults. Electrical issues often cause sudden valve failure.
System Performance
Valve failure impacts the entire system’s performance. Erratic pressure or flow signals valve problems. Equipment relying on the valve may work poorly or stop. Reduced system efficiency raises energy use and costs. Monitoring system behavior aids early valve issue detection.

Credit: startersolenoid.net
Key Checks Before Troubleshooting
Before starting solenoid valve troubleshooting, perform key checks to save time. These checks help identify simple problems that prevent valve operation. Confirming basic conditions avoids unnecessary disassembly or replacements. Focus on electrical connections, mechanical condition, pressure levels, and valve application. Each area affects valve performance and reliability.
Electrical Connections
Check the power supply to the solenoid coil. Ensure wires are firmly connected and not damaged. Measure voltage to confirm it matches valve specifications. Inspect the coil for signs of burning or corrosion. Loose or broken connections cause the valve to fail or act unpredictably.
Mechanical Condition
Inspect the valve body for dirt, debris, or corrosion. Clean any particles blocking the valve or ports. Look for worn or damaged seals and replace if needed. Check the plunger and spring movement; they should move freely without sticking. Mechanical faults often cause slow response or failure to open.
Pressure Levels
Verify the system pressure matches the solenoid valve’s rated range. Low or high pressure can prevent proper valve function. Use a pressure gauge to test inlet and outlet pressures. Confirm pressure is stable and within manufacturer limits. Incorrect pressure leads to leaks or incomplete valve operation.
Valve Application
Confirm the solenoid valve suits the specific application and fluid type. Check temperature ratings and compatibility with the media used. Using the wrong valve type causes premature failure and performance issues. Ensure the valve size matches flow requirements to avoid pressure drop or damage.
Fixing A Stuck Solenoid
A solenoid valve that sticks can disrupt your entire system. Fixing a stuck solenoid requires careful steps. These steps focus on cleaning, manual control, and checking key parts. Proper troubleshooting helps restore valve function quickly and safely.
De-energize And Clean
Start by turning off power to the solenoid valve. This prevents electrical shock and damage. Remove the valve from the system if possible. Clean dirt and debris from the valve body and plunger. Use a soft brush and mild cleaner to avoid damage. Make sure all parts move freely after cleaning.
Manual Override Use
Many solenoid valves have a manual override feature. This lets you open or close the valve manually. Use this to test if the valve can move without power. If the valve moves manually, the problem may be electrical. If it still sticks, the issue is likely mechanical.
Inspect Plunger And Spring
Check the plunger for signs of wear or corrosion. Look for damage or dirt that blocks movement. Inspect the spring for breaks or loss of tension. Replace any damaged parts with correct replacements. Clean parts carefully before reassembly to ensure smooth motion.
Check Voltage And Wiring
Measure the voltage at the solenoid coil using a multimeter. Confirm it matches the valve’s specifications. Examine wiring for loose connections or frayed insulation. Tighten connections and replace damaged wires. Proper voltage and wiring ensure the solenoid operates correctly.
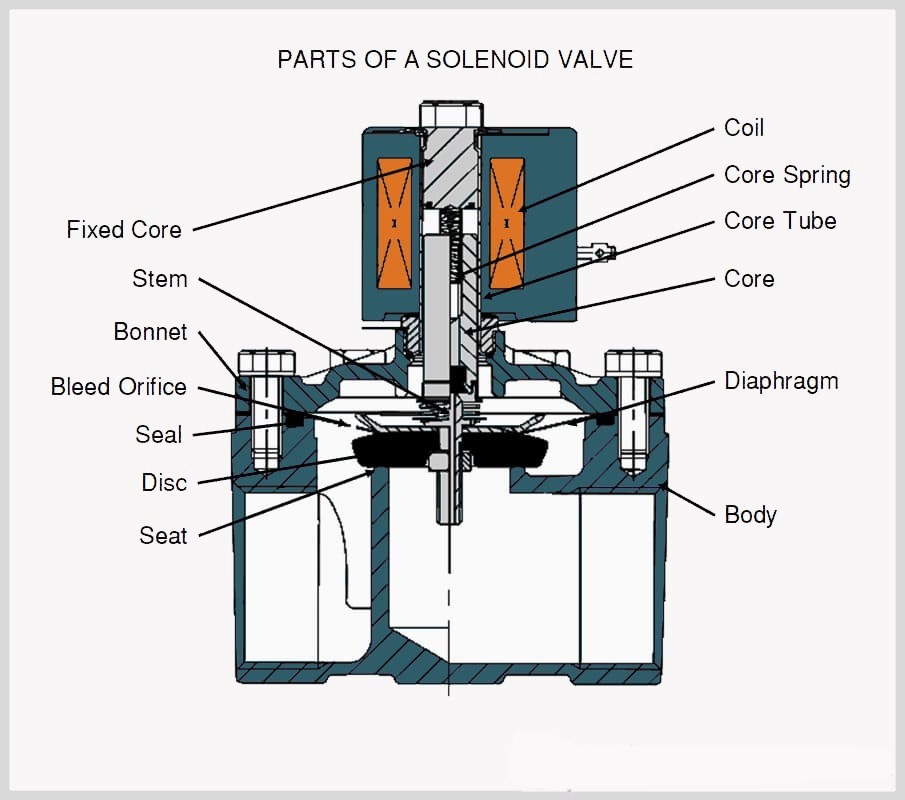
Credit: eltra-trade.com
Basic Troubleshooting Steps
Troubleshooting a solenoid valve starts with simple steps. These steps help find common problems fast. They also keep the process safe and effective. Follow these basic checks before deeper inspection or repair.
Power Off Safety
Always turn off power before inspecting the valve. This prevents electric shock or damage. Use a lockout device to ensure the power stays off. Check that all power sources are disconnected. Safety is the first priority in troubleshooting.
Manual Movement Test
Try moving the valve manually if it is safe to do so. This checks if the valve is stuck or jammed. Gently push or pull the valve plunger. If it moves smoothly, electrical issues might be the cause. If stuck, clean or replace parts as needed.
Voltage Verification
Use a multimeter to check the voltage at the solenoid coil. Compare the reading with the valve’s specifications. Low or no voltage means electrical problems like wiring or power supply faults. Correct voltage ensures the valve gets the power it needs to work properly.
Addressing Electrical Failures
Electrical failures are a common cause of solenoid valve malfunctions. These failures prevent the valve from operating correctly. Diagnosing and fixing electrical issues is crucial to restore valve function quickly. Simple checks often solve these problems without replacing the entire valve.
Coil Inspection
Start by examining the solenoid coil for visible damage. Look for signs of burning, melting, or discoloration. A damaged coil cannot generate the magnetic field needed to move the valve. Use a multimeter to test coil resistance. A reading too high or too low indicates a faulty coil. Replace the coil if it shows any defects.
Wiring Tightness
Loose or corroded wiring causes intermittent or no power to the coil. Check all electrical connections for tightness. Inspect terminals and connectors for rust or dirt. Clean corroded contacts with a wire brush or contact cleaner. Secure loose wires firmly to avoid electrical interruptions. Proper wiring ensures consistent valve operation.
Replacing Burnt Components
Burnt components can include fuses, connectors, or the coil itself. Identify burnt parts by their blackened or melted appearance. Replace any damaged fuses with the correct rating to protect the circuit. Swap out burnt connectors and wires to restore proper electrical flow. Always use compatible parts to maintain system safety.
Resolving Mechanical Issues
Mechanical issues often cause solenoid valves to malfunction. These problems reduce valve efficiency and can stop operations. Fixing mechanical faults helps restore normal valve function quickly. Troubleshooting focuses on common causes like debris, worn seals, and corrosion. Addressing these areas prevents further damage and extends valve life.
Removing Debris
Debris can block valve movement and stop it from opening or closing. Dirt, dust, and small particles often accumulate inside the valve. Clean the valve parts carefully using compressed air or a soft brush. Avoid harsh chemicals that may damage the valve. Regular cleaning keeps the valve working smoothly and prevents sticking.
Replacing Worn Seals
Seals wear out over time and cause leaks or poor sealing. Inspect the seals for cracks, tears, or hardening. Replace old seals with new ones made from compatible materials. Proper seal replacement stops leaks and improves valve pressure control. Always use manufacturer-recommended seals to ensure a tight fit and durability.
Corrosion Treatment
Corrosion damages valve surfaces and affects mechanical parts. Check for rust or discoloration on metal components. Remove corrosion with a wire brush or rust remover. Apply protective coatings or lubricants to prevent future rust. Corrosion treatment maintains valve integrity and prevents failures from metal degradation.
Testing And Monitoring Performance
Testing and monitoring the performance of a solenoid valve is vital for reliable operation. Regular checks help identify issues early and prevent costly downtime. These tests ensure the valve responds correctly under pressure, operates quietly, and maintains proper flow.
Pressure Response Checks
Pressure response checks verify if the valve opens and closes at the right pressure levels. Use a pressure gauge to measure the input and output pressures. The valve should respond immediately when the pressure changes. Delays or no response indicate possible blockages or coil failure. Accurate pressure response ensures smooth system operation and prevents damage.
Noise Detection
Listen carefully for unusual noises during valve operation. Humming, buzzing, or clicking sounds often signal electrical or mechanical problems. These noises can come from a worn coil, loose parts, or debris inside the valve. Quiet operation is a sign of a healthy valve. Detecting noise early helps avoid complete valve failure and costly repairs.
Flow Rate Verification
Flow rate verification checks if the valve allows the correct amount of fluid through. Measure the flow using a flow meter or by timing the output volume. A lower or inconsistent flow rate suggests partial blockage, internal leaks, or valve damage. Consistent flow rates confirm the valve works efficiently. Regular flow checks maintain system performance and safety.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Know If My Solenoid Valve Is Bad?
Check if the solenoid valve fails to open or close, leaks fluid, operates slowly, or makes unusual noises. Inspect electrical connections and for debris or corrosion.
How To Free Up A Stuck Solenoid?
De-energize the solenoid. Clean debris from the plunger and valve seat. Gently rock the plunger to free it. Check voltage and wiring. Inspect the internal spring. Use the manual override if available.
What Are The Common Solenoid Issues?
Common solenoid issues include failure to open or close, sticking, leaking, slow operation, unusual noises, electrical faults, and contamination.
How To Solve Solenoid Problem?
To solve a solenoid problem, first check voltage and wiring for faults. Clean debris from the plunger and valve seat. Inspect seals and springs for wear or corrosion. Verify system pressure and ensure proper valve sizing. Use manual override to free a stuck plunger if needed.
What Are Common Signs Of Solenoid Valve Failure?
Solenoid valves may fail to open or close properly, stick, leak fluid, or make unusual noises. Electrical issues or dirt inside can cause these problems. Watch for humming, buzzing, or slow valve response.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting solenoid valves helps keep systems running smoothly. Check electrical connections and coil condition first. Clean any dirt or debris blocking valve movement. Inspect seals and replace worn or damaged parts. Listen for unusual noises signaling internal problems. Regular maintenance avoids costly repairs and downtime.
Understanding common issues saves time and effort. Follow simple steps to restore valve function quickly. Stay alert to signs of valve failure for best results. Proper care extends valve life and system reliability.






